Communication between Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and lifts plays a crucial role in optimizing operations within factory floors. Particularly in the dynamic landscape of modern manufacturing facilities, efficient material handling is vital. DF Automation’s AMR stands out with its communication capabilities, and adapts to seamlessly interface with various lift types and meet diverse operational requirements.
This integration is instrumental in achieving the objectives of dark factories, where automation and efficiency are dominant. Our AMR is equipped with advanced functionalities that enable it to operate seamlessly within tiered factory floors, ensuring smooth navigation and timely delivery of goods. This not only boosts productivity but also minimizes downtime and errors in the production process.
DF AMR not only communicates effectively with lifts but also utilizes sensor technologies to assess real-time environmental conditions. By intelligently analyzing data regarding floor traffic, obstacle detection, and proximity to other machinery, the AMR optimizes its routes for maximum efficiency and safety. This data-driven approach ensures not only seamless material transportation but also proactive risk minimization, bolstering operational resilience in dynamic manufacturing environments.
Our automation solution for lifts optimizes workflow by automating the movement of goods between different levels of the factory, reducing manual intervention and streamlining processes. This not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes the risk of errors and delays associated with traditional material handling methods.
Moreover, by combining AMRs with lift operation capabilities, a new level of efficiency is unlocked. This integration not only streamlines material handling processes but also reduces operational costs by optimizing resource utilization and minimizing idle time through coordinated efforts.
Figure 1: Illustrates the Zalpha AMR navigating to a lift.
AMR Interface to Lift System
DF AMR offers a flexible interface to integrate with various lift systems, further enhancing its adaptability within factory environments. One significant method involves employing an external I/O interface, which enables the AMR to interact with lift controls effectively. Remote I/O modules are strategically added to the lift’s buttons and door sensors, allowing the AMR to simulate button presses and monitor door statuses. The AMR communicates with the DFleet server, which sets up the interaction with the lift system through a strong WiFi connection.
External I/O Interface:
A scenario of external I/O interface during an operation where the AMR needs to move from Level 1 to Level 2:
- The AMR arrives at the lift door on Level 1, triggering a simulated button press for Level 1 while awaiting confirmation of the door’s opening status.
- Upon verification, the AMR enters the lift on Level 1 while maintaining the simulated button press.
- As the lift ascends, the AMR releases the simulated button press at Level 1 and triggers a button press for Level 2, awaiting the corresponding door open signal.
- Upon reaching Level 2, the AMR exits the lift while still holding the simulated button press.
- Subsequently, the AMR releases the simulated button press and seamlessly proceeds with its designated operation.
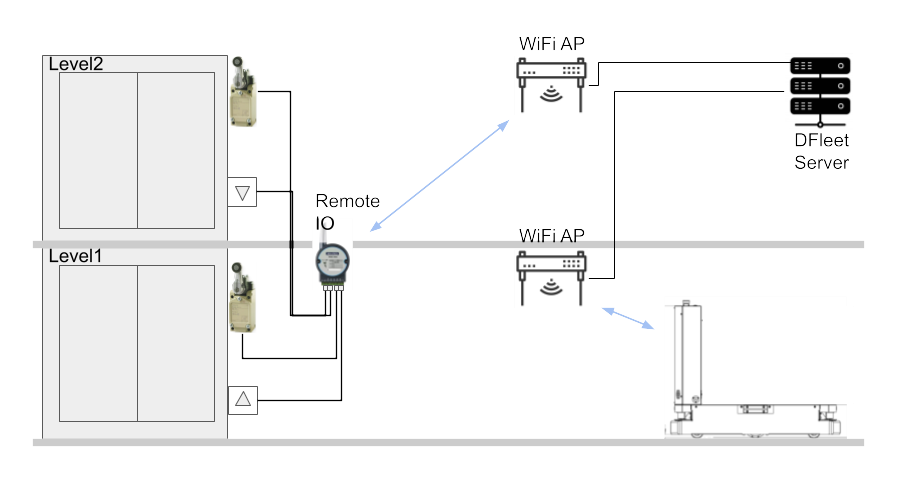
Figure 2: External I/O Interface of AMR communicates with lift.
Internal I/O Interface:
This method, a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or equivalent system is added depending on the Lift Controller interface type to facilitate communication between the AMR and the lift system. The internal I/O interface system serves to translate triggering signals from the DFleet server into commands compatible with the specific protocol of the lift controller. This interface system normally requires customization as the Lift Controller might require different interface protocol for the controls.
A scenario of internal I/O interface during an operation where the AMR needs to move from Level 1 to Level 2:
- Upon reaching the lift door on Level 1, the AMR initiates a call signal to prompt the lift’s movement to Level 1, awaiting confirmation of the lift’s arrival and door open signal from the Lift Controller.
- Once validated, the AMR enters the lift on Level 1 while maintaining the door open signal.
- As the lift ascends, the AMR releases the door open signal at Level 1 and triggers a call signal for the lift to proceed to Level 2, again awaiting confirmation of arrival and door open signal from the Lift Controller.
- Upon reaching Level 2, the AMR exits the lift while still holding the door open signal.
- Subsequently, the AMR releases the door open signal, seamlessly continuing with its designated operation.

Figure 3: Internal I/O Interface of AMR communicates with lift.
Multi-level Map & Teleport
To handle multi-level mapping, the NavWiz system supports more than one active map. During the setup phase, mapping for each level is done separately. Station configuration and path configuration in each map can also be edited and saved independently.
For AMR movement between levels, DF has developed a Teleport feature that allows the AMR to ‘teleport’ from one map to another, effectively moving from one level to another.
During path planning for an AMR to move between levels, the path planner automatically detects the need for teleportation. It then triggers the Teleport Task Template, which handles all interfaces to the Lift Controller. This process simplifies the configuration of the task template and allows it to be reused for different levels.
In essence, DF’s AMR with its communication capabilities and ability to navigate tiered factory floors effortlessly, exemplifies the transformative potential of integrating advanced technologies within industrial settings. As industries increasingly adopt automation and digitalization, the collaboration between AMRs and lifts contributes in streamlining material handling processes, and enhancing operational efficiency.
For more information, feel free to contact us via email at sales@dfautomation.com






















